Leetcode - 148. Sort List
August 13, 2021

문제
연결 리스트를 에 정렬하라.
Example 1.
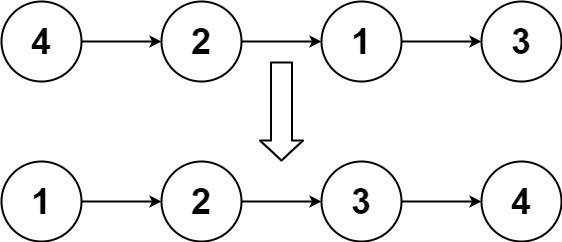
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]Example 2.

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]Example 3.
Input: head = []
Output: []나의 풀이
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
to_list = []
res = None
while head:
to_list.append(head.val)
head = head.next
to_list.sort(reverse=True)
for i in to_list:
res = ListNode(i, res)
return res
연결리스트를 Python List로 변환 후 Sorting하여 다시 새로운 연결리스트로 만들어 주었다.
풀이 : Merge sort
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def merge_two_lists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 and l2:
if l1.val > l2.val:
l1, l2 = l2, l1
l1.next = self.merge_two_lists(l1.next, l2)
return l1 or l2
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not (head and head.next):
return head
# using runner
half, slow, fast = None, head, head
while fast and fast.next:
half, slow, fast = slow, slow.next, fast.next.next
half.next = None
# 분할 재귀 호출
l1 = self.sortList(head)
l2 = self.sortList(slow)
return self.merge_two_lists(l1, l2)
Python에서는 연결 리스트 입력에 대해서 별도의 정렬 함수를 제공하지 않기 때문에 직접 정렬 알고리즘을 구현해야 한다.
다만 지문에 으로 풀어야 하기 때문에 버블 정렬은 사용할 수 없고 병합 또는 퀵 정렬정도를 생각할 수 있는데 연결 리스트는 특성상 피벗을 고정된 이취로 지정할 수 밖에 없고 입력 값에 따라 성능 편차가 심하므로 여기선 우선 병함 정렬로 구현하였다.
먼저 병합 정렬의 분할 정복을 위해서 먼저 중앙을 분할 해야하는데 연결리스트는 전체 길이를 알 수 없기 때문에 여기서는 런너 기법을 활용하였다.
half, slow, fast = None, head, head
while fast and fast.nect:
half, slow, fast = slow, slow.next, fast.next.next
half.next = Nonehalf, slow, fast 3개 변수를 만들어 두고 slow는 한 칸씩, fast는 두 칸씩 앞으로 이동한다. 이렇게 하면 fast가 끝에 도달했을때 slow는 중앙에 도착해 있을 것이다. 이때 half는 slow의 바로 이전 값으로 한다. 그리고 마지막에는 half.next = None으로 half위치를 기준으로 연결 리스트 관계를 끊어버린다.
이제 다음과 같이 분할해서 재귀 호출을 진행한다.
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
...
l1 = self.sortList(head)
l2 = self.sortList(slow)head는 시작 노드이고, slow는 런너 기법을 통해 발견한 중앙 지점이다. 이 값을 기준으로 계속 재귀 호출을 해나가면 결국 연결 리스트는 단일 아이템으로 모두 쪼개진다.
이제 이 쪼개진 아이템을 다시 합쳐서 리턴하는데 이때 그냥 합치는 것이 아니라 값을 비교 후 정렬하면서 이어 붙인다.
def merge_two_lists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 and l2:
if l1.val > l2.val:
l1, l2 = l2, l1
l1.next = self.merge_two_lists(l1.next, l2)
return l1 or l2
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
...
return self.merge_two_lists(l1, l2)여기서 merge_two_lists()메소드는 연결 리스트를 입력값으로 받아 길이가 얼마가 되든 재귀 호출을 통해 l1의 포인터를 이동하면서 정렬해 리턴한다.
여기서 return l1 or l2는 l1에 값이 있다면 항상 l1을 리턴하고 l1이 None인 경우 l2를 리턴한다.
>>> 1 or None
1
>>> 1 or 2
1
>>> None or 2
2다만, 실행 결과에서 알 수 있듯 내장 함수를 이용하는 방법보다 오히려 느리다는게 단점이다.
풀이 : 내장함수 sort( ) 사용
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
p = head
lst: List = []
while p:
lst.append(p.val)
p = p.next
lst.sort()
p = head
for i in range(len(lst)):
p.val = lst[i]
p = p.next
return head
내 풀이도 내장함수 sort()를 사용했지만 이 풀이와 다른점은 새로운 연결리스트를 생성하지 않고 주어진 연결리스트 head만 활용한 부분이다.
이렇게 하나의 연결리스트만 조작하니 나의 풀이보다 속도도 빠르고 공간복잡도에서도 더 유리한 것 같다.

